 Photo by rawpixel on Unsplash
Photo by rawpixel on Unsplash
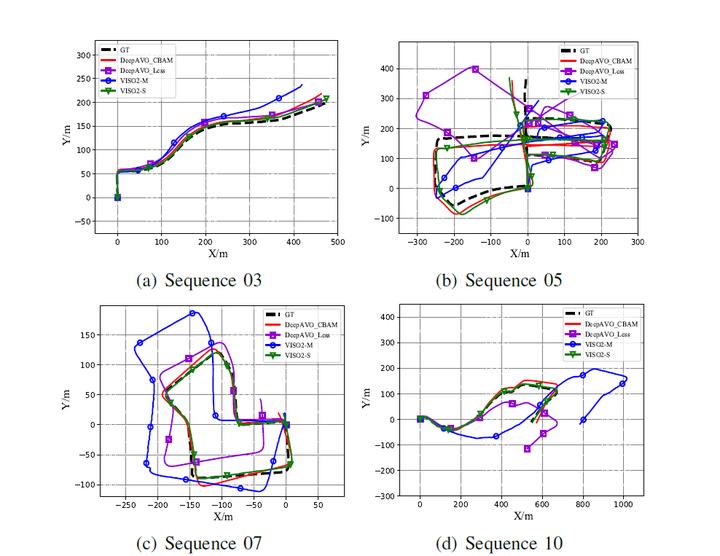
To build an intelligent robotic positioning system that can more efficiently deal with the traditional SLAM problems such as camera calibration, monocular scale ambiguity, we explore a novel strategy for performing visual ego-motion estimation based on deep learning. Here, we extend the model into four branches focusing on pixels movement in different directions in the optical flow and then regress the global feature concatenated from the four outputs to obtain F2F motion estimation. In particular, features extracted by each branch have been distilled by using the attention mechanism to refine estimation. Experiments on the KITTI and Malaga benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms state-of-the-art monocular methods by a large margin and produces competitive results against the classic stereo VO algorithm, which also highlights its promising generalization ability.